cholinergic neurons|cholinergic neurons meaning : Manila Nerve growth factor protects cholinergic neurons. The small non-toxic molecule urea has no neuroprotective effect on cholinergic neurons . See more Players will almost always be glad to see a Wild symbol, as these symbols substitute for others to generate additional wins. Sometimes they also . Ver mais
0 · where are cholinergic neurons found
1 · types of cholinergic receptors
2 · list of cholinergic drugs
3 · list examples of cholinergic neurons
4 · cholinergic neurons meaning
5 · cholinergic neurons location
6 · cholinergic neurons function
7 · cholinergic neuron wikipedia
Results History - Speedtest by Ookla - The Global Broadban.
cholinergic neurons*******A cholinergic neuron is a nerve cell which mainly uses the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to send its messages. Many neurological systems are cholinergic. Cholinergic neurons provide the primary source of acetylcholine to the cerebral cortex, and promote cortical activation during both . See morecholinergic neurons cholinergic neurons meaningMost research involving cholinergic neurons involves the basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. However, cholinergic neurons only represent about 5% of the total basal forebrain . See more
cholinergic neuronsNormal aging is described as aging unaccompanied by the behavioral or cognitive dysfunctions associated with the cholinergic basal forebrain system. In normal aging, there . See more
Cholinergic neurons, along with non-cholinergic neurons, have sleep/wake regulatory functions in the basal forebrain that can be categorized based on their firing patterns in . See moreNerve growth factor protects cholinergic neurons. The small non-toxic molecule urea has no neuroprotective effect on cholinergic neurons . See more
Degeneration of the cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain has been linked to progressing memory deficits related to aging, which . See more Cholinergic neurons are capable of producing ACh. An example of a central cholinergic area is the nucleus basalis of Meynert in the basal forebrain. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase converts .
Cholinergic neurons comprise a small population of cells in the striatum but have fundamental roles in fine tuning brain function, and in the etiology of neurological .Learn about cholinergic neurons in the CNS, their anatomy, function, and pathology. Explore chapters and articles from various books and journals on cholinergic neurons .
a, Overlapping pools of cholinergic neurons are located along the rostrocaudal extent of the basal forebrain in a manner that corresponds to their birthdate . The cholinergic midbrain is involved in a wide range of motor and cognitive processes. Cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine (PPN) and laterodorsal .
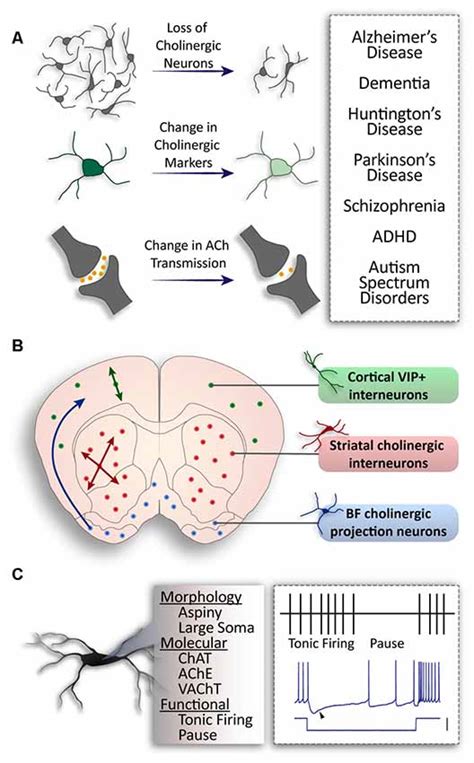
These cholinergic neurons can be divided into three main types: skeletal motor neurons, visceral motor neurons, and interneurons, with distinct functions in motor control 1. The two types of motor .
Cholinergic neurons are distributed widely in brain regions and play a role in cognitive function. ACh can regulate the normal cholinergic signal transduction associated with learning and memory. Patients with AD often manifest deficiency in ACh and damage to cholinergic signal transduction. Therefore, cholinergic signaling is a . The cholinergic midbrain is involved in a wide range of motor and cognitive processes. Cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine (PPN) and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT) send long-ranging . Cholinergic neurons are widely distributed in brain regions that play a role in cognitive functions and normal cholinergic signaling related to learning and memory is dependent on acetylcholine. The Locus Coeruleus norepinephrine (LC-NE) is the main noradrenergic nucleus that projects and supplies norepinephrine to different brain . The degeneration of cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain in the early stage of AD and the accompanying decline in memory and cognitive functions have become the basis for the formulation of one of the oldest theories of the etiology of AD – the cholinergic hypothesis (Davies and Maloney, 1976; Whitehouse et al., 1981, 1982; . Cholinergic is a term used to refer to the molecule acetylcholine. It is usually employed to define neurons, receptors or synapses that use acetylcholine. For instance, a cholinergic neuron is a neuron that releases acetylcholine, and a cholinergic receptor is a receptor to which acetylcholine binds. Acetylcholine is a signal molecule in the .The cholinergic system undergoes degeneration in adults with DS and the Ts65Dn mouse model. A large number of drugs have been developed to increase acetylcholine (ACh) in the AD brain, which shows the same changes in cholinergic neurons. Drugs that inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) have been used in individuals with DS. Cholinergic receptors function in signal transduction of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. . Within the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system, neurons are categorized as preganglionic and postganglionic, depending on the location of their cell bodies within the central or peripheral nervous systems. The N2 or . Using genetically labeled cholinergic neurons together with whole-brain reconstruction of optical images at 2-μm resolution, we obtained quantification of the number and soma volume of cholinergic neurons in 22 brain areas. Furthermore, by reconstructing the complete axonal arbors of fluorescently labeled single neurons from .
The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease centres on the progressive loss of limbic and neocortical cholinergic innervation. Neurofibrillary degeneration in the basal forebrain is believed to be the primary cause for the dysfunction and death of forebrain cholinergic neurons, giving rise to a widespread presynaptic .Cholinergic neurons densely innervate the hippocampus, mediating the formation of episodic as well as semantic memory. Here, we will review recent findings on acetylcholine’s modulation of memory function, with a particular focus on hippocampus-dependent learning, and the circuits involved. In addition, we will discuss the complexity .
Cholinergic neurons comprise a small population of cells in the striatum but have fundamental roles in fine tuning brain function, and in the etiology of neurological and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson's disease (PD) or schizophrenia. The process of developmental cell specification underlying neuronal identity and function is an area . The central cholinergic nervous system is the main neurotransmitter system in the brain and is composed of cholinergic neurons that can synthesize acetylcholine (ACh). Acetylcholine transferase (ChAT) is a marker enzyme for cholinergic neurons, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is synthesized in cholinergic neurons. In the rat model of epilepticus seizure, intraperitoneal pilocarpine injection promotes activation of cholinergic neurons and dysregulation of brain homeostasis (371–373). It is known to have no severe side effects in humans as a parasympathomimetic drug . Its role in modulating immunological components in infection, cancer, and .
A cholinergic neuron is a nerve cell which mainly uses the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to send its messages. Many neurological systems are cholinergic. Cholinergic neurons provide the primary source of acetylcholine to the cerebral cortex, and promote cortical activation during both wakefulness and rapid eye movement sleep. [1] .
In the CNS, the neurons that release and respond to ACh comprise the cholinergic system, which causes anti-excitatory effects. ACh plays a role in synaptic plasticity, including learning and short-term memory. ACh may bind either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors.

Cholinergic neurons comprise a small population of cells in the striatum but have fundamental roles in fine tuning brain function, and in the etiology of neurological and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease (PD) or schizophrenia.
As cholinergic neurons play an important role in activating brain regions via synchronous firing in the theta range, it may be one of the underlying processes that result in impaired cognition during aging. In the mammalian CNS, cholinergic neurons can be divided into three major classes: motor neurons, interneurons and projection neurons. Cholinergic motor neurons are dispersed. Cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine (PPN) and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT) send long-ranging axonal projections that target sensorimotor and limbic areas in the thalamus, the .Neuromuscular junctions, preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, the basal forebrain, and brain stem complexes are also cholinergic, as are the receptor for the merocrine sweat glands. In neuroscience and related fields, the term cholinergic is used in these related contexts:cholinergic neurons meaningCholinergic neurons are widely distributed in the brain and acetylcholine (ACh) binds to both central and peripheral cholinergic receptors. In this review we will primarily focus on cholinergic activity in the central nervous system (CNS).
Ep.1 อสุรกาย เสือจางซาน มาถึงแล้ว! อ่านเรื่องล่าสุดของ เทพเสือจางซาน จาก LINE WEBTOON เว็บไซต์อย่างเป็นทางการ ฟรี.
cholinergic neurons|cholinergic neurons meaning